Amorphous pockets are implemented as irregular shapes containing single neutral "native defects".
Once all the IV pairs have been recombined, the amorphous pockets tries to be dissolved. The particles not recombined wait for a dissolution event, calculated with the frequency:

Where:
λ is the jump distance.
D0AmorphousPocket is a prefactor in diffusivities units.
Edissol is the activation energy.
See symbol list.
When a mobile particle is near enough to the amorphous pocket (closer than the capture distance), it is captured by it and is inserted into it. See amorphous pocket interactions for further information.
Xn + X -> Xn+1
If the amorphous pocket has a large size (higher than a threshold), DADOS only counts the number of particles being captured by it (hidden particles), in order to save memory.
An impurity can also be captured by the amorphous pocket:
Interstitials and vacancies, however, can be recombined inside the structure. This is called dynamic annealing or shrinkage. This process is energetically more favorable than emission. The frequency associated to this event is given as follows (Mok et al. 2005):
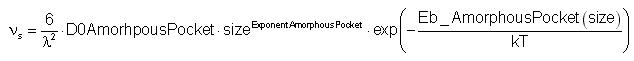
Where:
λ is the jump distance.
D0AmorphousPocket is a prefactor in diffusivities units.
"m" is the number of interstitials in the amorphous pocket.
"n" is the number of vacancies in the amorphous pocket.
size is the minimum between "m" and "n".
ExponentAmorphousPocket is an exponent.
Eb_AmorphousPocket is the activation energy.
See symbol list.