Point defects can be:
Break-up is a mechanism for splitting a point defect: Ai -> A + I or AV -> A + V.
The break-up frequency is calculated by DADOS with an Arrhenius plot:
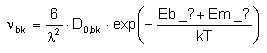
Where:
A capture can occur when a particle or defect is sufficiently near to another particle or defect and the capture is allowed. DADOS uses a capture distance called λ.
If the particle arrives in a very populated area, where more than one interaction is possible, DADOS randomly selects one.
A capture is always associated to an interaction.
For extended defects, such as amorphous pockets, I311, dislocation loops or voids, the captures depend on the surface, because it is there where the interaction occurs. Therefore, the larger the surface is, the capture will happen more frequently.
Mobile particles in DADOS jump at a rate that is determined by both energy and temperature.
The implemented jumping directions are six: +x, -x, +y, -y, +z, -z.
Jump distance
Jump distance is called λ. We take it also to be equal to the capture distance.
Its value is 0.384 nm, corresponding to the second neighbors distance in the silicon lattice.
It is involved into the relation between the migration rate and the diffusivity:
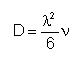
Jump frequency
Jump frequency is calculated by using Em_? and Dm_?:
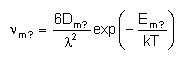
Where:
When a mobile dopant meets an amorphous pocket or an extended defect (I311 or void), the interstitial or vacancy is included into the extended defect whereas the dopant keeps very near to the defect but not included in it. It is, then, simulated as a point defect.