Voids are implemented in DADOS as spherical-shaped structures of immobile vacancies.
Voids emit vacancies by taking one from the edge and releasing as a point defect it at any point randomly chosen in the edge. The emission rate is:
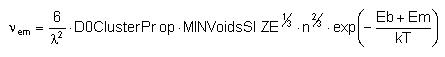
Where:
λ is the jump distance.
When a mobile vacancy is near enough the void (closer than the capture distance), it is captured by it and is inserted into the edge of the structure.
When a mobile interstitial is near enough the void, it is captured by it and it is recombined with a vacancy. When only one particle is remaining, the void is transformed into a point defect.